Introduction
In recent years, the supply chain industry has faced increasing challenges. From product counterfeiting to delayed shipments, inefficiencies in supply chain management have become a growing concern for businesses worldwide. One technology that promises to revolutionize this space is blockchain. Blockchain in supply chain is not just a buzzword it offers practical solutions for transparency, security, and efficiency.
Unlike traditional systems that rely on centralized databases, blockchain provides a decentralized and tamper-proof ledger. This allows businesses, suppliers, and consumers to track every step of a product’s journey in real-time. The result is reduced fraud, faster operations, and greater trust across the network.
What is Blockchain in Supply Chain?
Blockchain in supply chain refers to the use of blockchain technology to record, verify, and share information about products as they move through the supply chain. Each transaction or movement is recorded on a digital ledger, which is immutable, transparent, and accessible to authorized participants.
Here’s a simple example: imagine a coffee bean traveling from a farm to a coffee shop. With blockchain, every step—from harvesting, processing, shipping, to delivery—is recorded. Retailers and consumers can verify the origin and quality of the product, reducing fraud and ensuring accountability.
Key features of blockchain in supply chain include:
- Decentralization: No single authority controls the data.
- Transparency: All parties can view and verify transactions.
- Immutability: Records cannot be altered once entered.
- Traceability: Complete history of the product’s journey is available.
By implementing blockchain, businesses can eliminate paper-based processes, reduce errors, and increase operational efficiency.
Why is Blockchain in Supply Chain Important?

Blockchain in supply chain is important because it addresses some of the most pressing challenges faced by the logistics and manufacturing industries. Traditional supply chains often suffer from inefficiencies due to lack of transparency, poor communication, and reliance on manual processes.
Here are key reasons why blockchain matters:
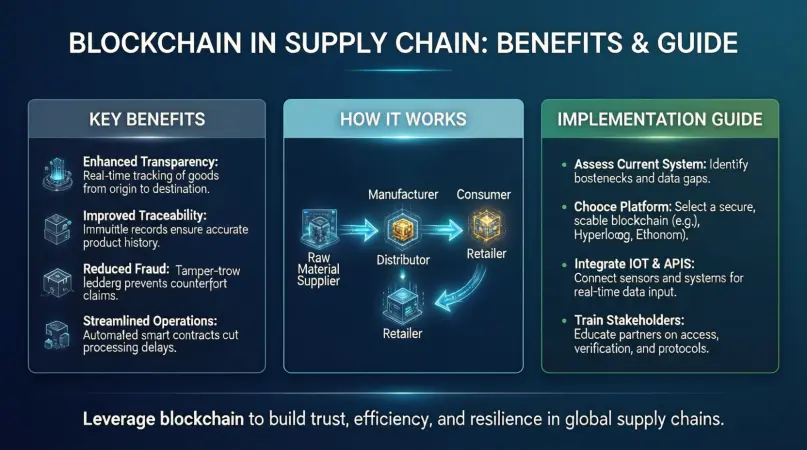
- Enhanced Transparency: All participants have access to the same information, reducing disputes and errors.
- Fraud Prevention: Immutable records make it nearly impossible to tamper with data.
- Traceability: Products can be traced from origin to endpoint, ensuring quality and authenticity.
- Cost Reduction: By automating verification processes, blockchain reduces administrative costs.
- Improved Collaboration: Stakeholders can share real-time information securely, enhancing coordination.
In industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and luxury goods, where authenticity and safety are critical, blockchain provides a trusted system for verifying every transaction.
Detailed Step-by-Step Guide to Implement Blockchain in Supply Chain
Implementing blockchain in supply chain requires careful planning and execution. Here is a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Identify Supply Chain Challenges
Before adopting blockchain, identify the key issues in your supply chain. Common problems include:
- Counterfeit products
- Delayed shipments
- Inaccurate inventory tracking
- Inefficient record-keeping
Step 2: Choose the Right Blockchain Platform
Not all blockchains are the same. You need a platform suitable for your business needs. Popular options include:
- Hyperledger Fabric: Ideal for private supply chain networks.
- Ethereum: Suitable for smart contract automation.
- Corda: Focused on enterprise-grade applications.
Step 3: Define Data to be Tracked
Determine what data needs to be recorded on the blockchain. Examples include:
- Product origin
- Manufacturing details
- Shipment dates
- Quality checks
Step 4: Integrate IoT and Sensors
IoT devices can automatically capture real-time data, such as temperature, humidity, and location. This ensures accurate tracking and reduces human error.
Step 5: Create Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements that trigger actions when conditions are met. For example:
- Automatically release payment when goods are delivered.
- Send alerts if temperature limits are exceeded during transport.
Step 6: Onboard Stakeholders
All participants in the supply chain—including suppliers, transporters, and retailers—must be onboarded to the blockchain network. Provide training to ensure smooth adoption.
Step 7: Monitor and Optimize
Once implemented, continuously monitor the system for performance and improvements. Use analytics to identify bottlenecks and optimize processes.
Benefits of Blockchain in Supply Chain
Blockchain in supply chain offers numerous benefits for businesses and consumers alike. Key advantages include:
- Transparency: All stakeholders have access to the same information.
- Security: Data is encrypted and tamper-proof.
- Traceability: Complete visibility of the product journey.
- Reduced Costs: Automates manual processes and reduces paperwork.
- Faster Transactions: Eliminates intermediaries, speeding up payments and approvals.
- Improved Compliance: Easy to demonstrate adherence to regulations.
- Better Customer Trust: Verified product origins improve consumer confidence.
For instance, Walmart uses blockchain to trace produce from farm to store, reducing the time to track an item from seven days to just 2.2 seconds.
Disadvantages / Risks of Blockchain in Supply Chain
While blockchain offers many advantages, it also has challenges:
- High Implementation Cost: Initial setup and training can be expensive.
- Scalability Issues: Large networks may experience slower transaction speeds.
- Integration Challenges: Connecting blockchain with existing systems can be complex.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Different regions have varying blockchain regulations.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Sharing sensitive business data across a network can be risky.
- Skill Gap: Limited availability of blockchain expertise can slow adoption.
Understanding these risks helps businesses make informed decisions and develop effective strategies for mitigation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When implementing blockchain in supply chain, avoid these mistakes:
- Ignoring Stakeholder Buy-In: Success depends on all participants embracing the technology.
- Overcomplicating the System: Focus on essential data first; unnecessary complexity can hinder adoption.
- Neglecting Compliance: Ensure alignment with local laws and industry standards.
- Not Testing Properly: Pilot programs help identify issues before full-scale deployment.
- Underestimating Costs: Factor in software, hardware, and training expenses.
- Failing to Update Continuously: Blockchain networks require regular monitoring and optimization.
Avoiding these mistakes ensures smoother implementation and faster realization of benefits.
FAQs about Blockchain in Supply Chain
1. How does blockchain improve supply chain transparency?
Blockchain records every transaction in a decentralized ledger accessible to all authorized participants. This ensures everyone sees the same data, reducing errors and disputes.
2. Can small businesses benefit from blockchain in supply chain?
Yes. Even small businesses can gain transparency, reduce fraud, and streamline operations by using blockchain platforms tailored for small networks.
3. How long does it take to implement blockchain in supply chain?
Implementation varies depending on complexity, stakeholder size, and system integration. Small pilots can take 2–3 months, while full-scale adoption may take 6–12 months.
4. Are there environmental concerns with blockchain?
Some blockchain platforms, especially proof-of-work systems, consume significant energy. Choosing eco-friendly alternatives like proof-of-stake or private blockchains mitigates this concern.
5. What industries can benefit most from blockchain in supply chain?
Industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, luxury goods, and electronics benefit most due to high demand for traceability, authenticity, and compliance.
6. How secure is blockchain for supply chain data?
Blockchain is highly secure due to encryption, decentralization, and immutability. However, network security and access control are still essential.
7. Can blockchain reduce counterfeit products?
Yes. Blockchain provides verifiable records of product origin and ownership, making it difficult for counterfeit goods to enter the supply chain.
8. Is blockchain compatible with existing supply chain systems?
Yes, but integration may require middleware or APIs. Planning and testing are crucial to ensure smooth connectivity.
Expert Tips & Bonus Points
- Start Small: Pilot blockchain on a single product line before scaling.
- Use IoT Devices: Automate data collection for accuracy.
- Leverage Smart Contracts: Reduce manual approvals and speed up transactions.
- Collaborate with Partners: Ensure all stakeholders are aligned and trained.
- Monitor and Improve: Regularly analyze performance data for continuous improvement.
- Focus on ROI: Prioritize areas where blockchain delivers measurable value.
- Stay Updated: Blockchain technology evolves rapidly; staying informed ensures competitiveness.
Bonus: Combining blockchain with AI and predictive analytics can further enhance supply chain efficiency and decision-making.
Conclusion
Blockchain in supply chain is no longer a futuristic concept; it is a practical tool for improving transparency, efficiency, and trust. By recording every transaction on a secure and immutable ledger, businesses can reduce fraud, cut costs, and optimize operations. While implementation requires careful planning, investment, and stakeholder buy-in, the long-term benefits far outweigh the challenges.
For businesses aiming to remain competitive in today’s global market, adopting blockchain in supply chain is a strategic move. It ensures accountability, enhances customer trust, and opens new opportunities for innovation. With proper execution, blockchain can transform the way products are sourced, shipped, and delivered, making supply chains smarter, faster, and more reliable.